#Water Conservation
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
From the article:
The two students presented their groundbreaking project at the 2024 International Science and Engineering Fair (ISEF); a device that operates by using ultrasound waves to push microplastic particles to one side of a water flow, allowing clean water to pass through while trapping the contaminants. In their tests, the system successfully captured up to 94 per cent of microplastic particles, showing promise for real-world applications. "If we could refine this, maybe use more professional equipment, maybe go to a lab instead of testing from our home, we could really improve our device and get it ready for large-scale manufacturing," Justin told Business Insider. The duo envisioned their device being used in water treatment plants, directly modifying the quality of water for daily use. This application could significantly reduce the amount of microplastics that end up in water sources, protecting ecosystems and human health.
#microplastics#water filtration#plastics#plastic pollution#pollution#good news#environment#sustainability#hope#hopepunk#ecology#water conservation
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Dandelion News - February 15-21
Like these weekly compilations? Tip me at $kaybarr1735 or check out my Dandelion Doodles!
1. Solar farms managed for nature boost bird abundance and diversity, new study finds

“There were more than twice as many farmland birds in the well-managed solar farms compared with the intensively farmed land, and nearly 16 times as many woodland birds. […] Overall, diversity was 2.5 times higher, while woodland birds were nine times more diverse.”
2. Washington judge blocks Trump’s gender-affirming care ban, says it's unconstitutional in multiple ways

“This marks the second time in a week that a judge has stood in the way of Trump’s attacks on trans kids. [… The ruling grants] a temporary restraining order that halts enforcement of provisions in Trump’s directive that would cut off federal funding to medical institutions that provide gender-affirming care to minors.”
3. Fog harvesting could provide water for arid cities

“17,000 sq m of mesh could produce enough water to meet the weekly water demand of [… the] urban slums. 110 sq m could meet the annual demand for the irrigation of the city's green spaces. Fog water could be used for soil-free (hydroponic) agriculture, with yields of 33 to 44lb (15 to 20kg) of green vegetables in a month.”
4. Audubon Applauds Bipartisan Federal Effort to Protect Delaware River Basin with Critical Reauthorization Bill

“The bill would […] ensure long-term conservation and restoration efforts, expand the official definition of the basin to include Maryland, and prioritize projects that serve small, rural, and disadvantaged communities. […] The watershed provides important year-round habitats and critical migratory stopovers for approximately 400 bird species[….]”
5. mRNA vaccines show promise in pancreatic cancer in early trial
“Half of the people in the study — eight of the participants — responded to the vaccine, producing T cells that targeted their tumors. […] Just two of the patients who had a response to the vaccine had their cancer return during the three-year follow- up, compared to seven of the eight who did not respond to the vaccine treatments.”
6. Minn. Lt. Gov. Flanagan Makes It Official; She's running for U.S. Senate

“[Flanagan has] “championed kitchen-table issues like raising the minimum wage, paid family and medical leave, and free school meals.” If elected, Flanagan, a tribal citizen of the White Earth Nation, would become the first Native American female U.S. senator in history.”
7. Federal Funding Restored for Low-Income Alabama Utility Assistance After Outcry

“A program meant to help low-income Alabamians pay their utility bills has resumed two weeks after it was canceled due to an executive order from President Donald Trump. […] “We can confirm the funds are reaching those affected by the previous pause[….]””
8. Modeling study suggests Amazon rainforest is more resilient than assumed

“[Previous] studies were either conducted with global climate models that used a simplified representation of convection [or were on a regional scale….] According to the computations, mean annual precipitation in the Amazon does not change significantly even after complete deforestation.“
9. States are moving forward with Buy Clean policies despite Trump reversal

““Buy Clean is a great example of how states and other nonfederal actors can continue to press forward on climate action, regardless of what the federal government does,” said Casey Katims, executive director of the U.S. Climate Alliance, a bipartisan coalition of two dozen governors.”
10. The rewilded golf courses teeming with life

“A wildflower meadow, ponds, scrub habitat, coastline and even an area of peat bog can be found on this little 60-acre (24-hectare) plot, which boasts roe deer, otters, lizards, eels and a huge array of insects and birds.”
February 8-14 news here | (all credit for images and written material can be found at the source linked; I don’t claim credit for anything but curating.)
#hopepunk#good news#nature#us politics#solar power#solar panels#solar energy#birds#biodiversity#gender affirming care#transgender#trans rights#trans healthcare#water conservation#habitat#migratory birds#vaccines#vaccination#mrna vaccine#pancreatic cancer#cancer#native american#alabama#low income#amazon rainforest#rainforest#executive orders#climate action#golf course#habitat restoration
981 notes
·
View notes
Text
"High along the peaks and ridges of the mountains in Ecuador, a 25-year-long conservation program is bearing succulent fruit in the form of cleaner water and abundant wildlife.
Established in the year 2000, Quito’s fund for the protection of water has allowed a critical South American ecosystem unique to the world and vital to both plants and animals to reclaim vast tracts of its former landscape, and people are noticing the difference.
“Before the water fund, the páramo in Antisana was very degraded. The only thing you would see was sheep.” Silvia Benitez, the Nature Conservancy’s Director of Freshwater for Latin America, said in a statement. “The change has been amazing. Vegetation is back. The wetlands are restored.”
“Now people see groups of deer. They see puma. I saw a fox. I had never before seen a fox in this area.”
The story of this quarter-century success began when the United States nonprofit the Nature Conservancy partnered with Quito’s water utility company, known as EPMAPS. The second-highest capital city on Earth by altitude, Quito is surrounded by a famous ecosystem called the páramo, a biodiversity hotspot where masses of mosses, lichen, high-altitude palms, and endemic grasses create a mountain environment unlike any other.
The páramo covers slopes above 10,000 feet in elevation all over the Andes Mountains, and acts like a giant sponge absorbing and condensing moisture from the lower ground before releasing it in streams and rivers further down. The Nature Conservancy estimates that in Colombia, where páramos cover just 2% of land area, this hydrological service provides 70% of all municipal water. It’s estimated that páramo sequesters 6 times more carbon than tropical rainforest.
EPMAPS and the Nature Conservancy organized $21,000 in seed money to kick-start a trust fund that would charge downstream users of water from the páramos around Quito for the conservation measures needed to protect them.
Called the Fund for the Protection of Water, or FONAG, it’s accumulated $2.5 million in annual contributions over the last 25 years, and as a result, páramos are retaking ranchland that once displaced them, and the wildlife like whitetail deer, Andean bears, Mountain tapirs, and condors are returning as well.
“Since FONAG’s beginning, its priority has always been the protection of the water sources. But when you conserve water sources, it’s almost automatic that you have other co-benefits—biodiversity, carbon sequestration, and social benefits,” said Bert de Bievre, Technical Secretary of FONAG.
Local communities have become very involved in FONAG’s work. Two dozen have become páramo rangers, local ranchers have moved their animals to lower elevations, agriculturalists have worked with EPMAPS to switch to low-impact methods of cultivation away from watersheds, and the Nature Conservancy runs a nursery that grows many of the endemic páramo plants for use in reforestation.
The Quito-FONAG model is now being implemented across the northwestern areas of South America, and it shows how much can be achieved by simply letting rivers run free.
“Each year, the global water sector spends $700 billion on building and repairing pipes and reservoirs, using grey solutions to engineer themselves out of a problem created by deforestation, agriculture or other threats upstream,” said Brooke Atwell, Associate Director of the Nature Conservancy’s Resilient Watersheds strategy.
“If we were able to reallocate just 1% of that spending ($7 billion) toward protecting nature, it would eclipse all global philanthropic spending on conservation today.”"
-via Good News Network, April 1, 2025
#ecuador#south america#quito#quitoecuador#rivers#ecosystem#ecosystem restoration#water#biodiversity#endangered species#water conservation#good news#hope
697 notes
·
View notes
Text
#china#good news#environmentalism#science#environment#nature#animals#conservation#climate change#climate crisis#birds#erosion#soil erosion#water conservation#soil conservation#loess plateau
265 notes
·
View notes
Text

With the country now at war, Mayor LaGuardia launched a city campaign to conserve water. This was one of a number of ads (for the subway, presumably) designed by Earl Kerkam, ca. 1942.
Photo: LMPC/Getty Images/Zazzle
#vintage New York#1940s#Earl Kerkam#vintage poster#World War II#home front#water conservation#conserve water#1940s New York#WWII at home#subway ad
211 notes
·
View notes
Text

If there is magic on this planet, it is contained in water
- LOREN EISELEY
#water view#water art#water conservation#water everywhere#water energy#water element#water is life#water magic#water nymph#toya's tales#style#toyastales#toyas tales#art#july#summer#red and blue#red carpet#area rug#handmade rug#carpets and rugs#persian rugs#water quality#water reflection#water resources#water restoration#water ripples#water rights#water tribe#nature
259 notes
·
View notes
Text
*casually posts this at the same time to further my agenda of growing native plants instead of grass and shitty ornamentals*





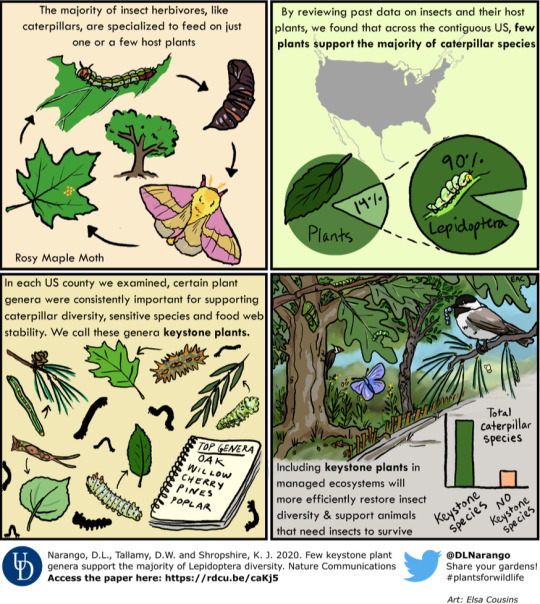

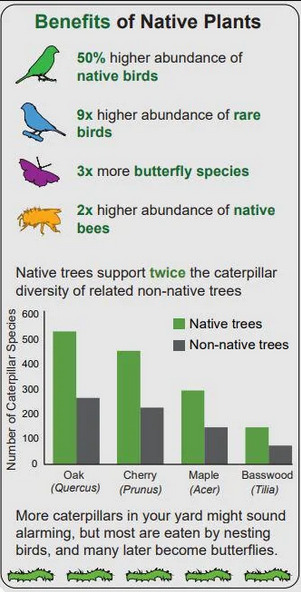

#gardening#water conservation#biodiversity#kill your lawn#native plants#native pollinators#pollinator garden#climate change#sustainability#environmental rehabilitation#habitat restoration#wildflowers#native flowers#animals#water crisis#didnt mean to post that grass one whoops. i think i skimmed it and wasnt thinking about it too much#but ig its true grass would be better than roads. lets just uh. make it native grass yaknow?
299 notes
·
View notes
Text
hey do you live in utah please take this survey!!! aug 2023
if you do please take this government survey about water usage, housing development, and public transit development in the near future!

particular things to watch for:
should we require low-water-use landscaping on new development
should we require existing wasteful landscaping for businesses and home developments be replaced with low-water-use landscaping
encouraging field fallowing -- currently utah's policy means a farmer can lose water rights on a field if they don't water it every year even if theyre not growing somwthing. fallowing would allow for people to let fields rest by not planting or watering on off years, massively reducing water waste
encouraging public transport in the form of fareless buses and trains, increasing pedestrian areas and bike lanes
reducing highway development thank god
developing dead malls and huge parking lots into more housing and pedestrian areas
please take it it's not terribly long and is pretty well formatted so it's easily digestible! utahs water policy and development has been ATROCIOUS lately this could really shape the future into something better. if u dont live in utah sharing would be appreciated <3
#birdenest#important#utah#water conservation#queerstake#<- i know a lot of those people live in utah so im tagging yall lol
140 notes
·
View notes
Text
Grey Water Recycling Systems: Your Guide to Sustainable Water Management at Home
As environmental awareness grows, homeowners and businesses alike are seeking ways to conserve resources and reduce their ecological footprints. One highly effective solution is implementing a grey water recycling system. Grey water systems allow you to reuse water from sinks, showers, and washing machines for non-potable purposes, reducing both water consumption and utility costs. In this…
#Benefits of grey water reuse#DIY grey water system#Eco-friendly water systems#Grey water irrigation#Grey water recycling system#Grey water regulations#Grey water reuse#Grey water systems#Grey water systems for home#Grey water treatment#Household water recycling#How to install a grey water recycling system#Safe use of grey water in gardens#Sustainable water management#water conservation
17 notes
·
View notes
Text

Stilled Life of Water.
©Robin Fifield 2024.
#robin fifield photography#photographers on tumblr#awehaven#still life#water photography#water#water conservation#water a human right#water texture#water supply#flow like water
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
Earthships - America's Off-Grid Desert Community
youtube
#off grid#self sustainability#sustainable living#sustainability#sustainable#earthship#earth friendly#video#water conservation#alternative living#alternative energy#alternative construction#garbage#garbage warrior#recycling#Youtube
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
From the article:
“We really kind of refer to this as our third aqueduct,” says John Bednarski, an interim assistant general manager at the Metropolitan Water District of Southern California — a powerful agency, as the largest wholesale provider of water in the nation and owner of the Colorado River Aqueduct. The “third aqueduct” Bednarski is referring to is not another man-made appendage stretching to the Colorado River Basin or into Northern California but rather a project that’s designed to stay local — and sustainable: Pure Water Southern California would recycle wastewater, treat it and produce 150 million gallons of water each day, accounting for about 10 percent of the agency’s local water demands, according to Bednarski. “So it’s going to be a major contributor,” he says. [...] The L.A. Department of Water and Power is pursuing a similar recycling project. And in 2022, 26 cities and wholesale water providers that pull from the Colorado River wrote a memorandum of understanding committing to focusing on water recycling and reuse. The signatories, including Metropolitan, often point to Las Vegas as a model for recycling wastewater to reduce its total Colorado River use and increase the amount of water available for use. Nevada has long faced scarcity; of all the states, it receives the smallest share of the river: just 1.8 percent of all the water rights. By treating and reusing nearly all of its indoor water, the Las Vegas water purveyor effectively uses the same water over and over, expanding its supply. Now Las Vegas officials, along with Arizona water managers, are looking to the Pure Water project to further shore up supplies on the Colorado River. Their thinking: If Metropolitan can reduce its Colorado River use, its unused water could flow to Nevada and Arizona, providing a needed boost in an era when there is little to spare. In that way, water recycling projects in one area can have consequences across watersheds."
#wastewater recycling#water conservation#resource management#climate resilience#climate change#global warming#climate change resilience#renewable resources#water resources#drought#environment#good news#hope#solutions#climate solutions
187 notes
·
View notes
Text
Dandelion News - November 1-7
Like these weekly compilations? Tip me at $kaybarr1735 or check out my Dandelion Doodles on Patreon!
1. Climate Initiatives Fare Well Across the Country Despite National Political Climate

“[California voters approved] a $10 billion bond measure to boost climate resilience across [the] state[…. Hawai’i] voters cast their ballots in favor of establishing the [climate] resiliency fund, with money for the project coming from existing property tax revenue.“
2. ‘You have to disguise your human form’: how sea eagles are being returned to Severn estuary after 150 years

“[… To avoid imprinting,] the handlers will wear long robes and feed the young eagles chopped rabbit and other meat with bird hand-puppets. […] Williams hopes that restoring eagles to the top of the food chain in the estuary will create a more balanced, thriving ecosystem.”
3. 10 states voted on pro-abortion referendums. 7 of them passed

“New York voters overwhelmingly approved the Equal Rights Amendment, adding [… among other characteristics] gender expression, pregnancy, and pregnancy outcomes to anti-discrimination laws. […] In deep-red Missouri and Montana, voters also enshrined abortions protections in their state constitutions.”
4. Giant rats could soon fight illegal wildlife trade by sniffing out elephant tusk and rhino horn

“”Our study shows that we can train African giant pouched rats to detect illegally trafficked wildlife, even when it has been concealed among other substances[.…] They can easily access tight spaces like cargo in packed shipping containers or be lifted up high to screen the ventilation systems of sealed containers,” Szott explained.”
5. Sarah McBride wins Delaware U.S. House seat, becoming the first out trans member of Congress

“McBride spearheaded Delaware’s legislation to ban the “gay and trans panic” defense as a state senator [… and] helped to pass paid family and medical leave, gun safety measures, and protections for reproductive rights.”
6. Critically endangered Sumatran elephant calf born in Indonesia

“Indonesian officials hailed the births and said they showed conservation efforts were essential to prevent the protected species from extinction. […] Sumatran elephants are on the brink of extinction with only about 2,400-2,800 left in the world, according to the World Wide Fund for Nature.”
7. Sin City is Going Green

“[Hotels there] have conserved 16 billion gallons of water since 2007, thanks to […] replacing grass with desert-friendly landscaping, installing water-efficient taps across all properties, and reusing water at aquariums and in the Bellagio Fountain.”
8. Gray squirrel control: Study shows promise for effective contraceptive delivery system

“[… T]he feeders have a very high level of species-specificity. […] The bait and monitoring system developed and tested in the study demonstrated that […] “spring was the only season tested where female squirrels were more likely to visit bait feeders than males. Spring coincides with a peak in squirrel breeding and is therefore a good time to deliver a contraceptive."”
9. Returning Grazing Land to Native Forests Would Yield Big Climate Benefits

“[… S]trategically regrowing forests on land where cattle currently graze […] while intensifying production elsewhere could drastically cut greenhouse gas emissions, with little hit to global protein production, a new study shows.”
10. Interior Department Strengthens Conservation of American Bison Through New Agreement with Canada and Mexico

“Approximately 31,000 bison are currently being stewarded by the United States, Canada and Mexico with the goal of conserving the species and their role in the function of native grassland systems, as well as their place in Indigenous culture.”
October 22-28 news here | (all credit for images and written material can be found at the source linked; I don’t claim credit for anything but curating.)
#hopepunk#good news#voting#climate#climate change#eagles#abortion rights#abortion#rats#giant rat#sarah mcbride#congress#trans rights#transgender#elephant#endangered species#las vegas nevada#water conservation#squirrel#cattle#livestock#bison#canada#mexico#indonesia#nature#us politics#animals#sin city#missouri
281 notes
·
View notes
Text
Legit though, we should start turning ecosystem restoration and work to make our world more tolerant to the effects of climate change into annual holidays and festivals
Like how just about every culture used to have festivals to celebrate the beginning of the harvest or its end, or the beginning of planting, or how whole communities used to host barn raisings and quilting bees - everyone coming together at once to turn the work of months or years into the work of a few days
Humble suggestions for festival types:
Goat festival
Besides controlled burns (which you can't do if there's too much dead brush), the fastest, most effective, and most cost-efficient way to clear brush before fire season - esp really heavy dead brush - is to just. Put a bunch of goats on your land for a few days!
Remember that Shark Tank competitor who wanted to start a goat rental company, and everyone was like wtf? There was even a whole John Oliver bit making fun of the idea? Well THAT JUST PROVES THEY'RE FROM NICE WET PLACES, because goat rental companies are totally a thing, and they're great.
So like. Why don't we have a weekend where everyone with goats just takes those goats to the nearest land that needs a ton of clearing? Public officials could put up maps of where on public lands grazing is needed, and where it definitely shouldn't happen. Farmers and people/groups with a lot of acres that need clearing can post Goat Requests.
Little kids can make goat-themed crafts and give the goats lots of pets or treats at the end of the day for doing such a good job. Volunteers can help wrangle things so goats don't get where they're not supposed to (and everyone fences off land nowadays anyway, mostly). And the goats, of course, would be in fucking banquet paradise.
Planting Festival and Harvest Festival
Why mess with success??? Bring these back where they've disappeared!!! Time to swarm the community gardens and help everyone near you with a farm make sure that all of their seeds are sown and none of the food goes to waste in the fields, decaying and unpicked.
And then set up distribution parts of the festival so all the extra food gets where it needs to be! Boxes of free lemons in front of your house because you have 80 goddamned lemons are great, but you know what else would be great? An organized effort to take that shit to food pantries (which SUPER rarely get fresh produce, because they can't hold anything perishable for long at all) and community/farmer's markets
Rain Capture Festival
The "water year" - how we track annual rainfall and precipitation - is offset from the regular calendar year because, like, that's just when water cycles through the ecosystems (e.g. meltwater). At least in the US, the water year is October 1st through September 30th of the next year, because October 1st is around when all the snowmelt from last year is gone, and a new cycle is starting as rain begins to fall again in earnest.
So why don't we all have a big barn raising equivalent every September to build rain capture infrastructure?
Team up with some neighbors to turn one of those little grass strips on the sidewalk into a rain-garden with fall-planting plants. Go down to your local church and help them install some gutters and rain barrels. Help deculvert rivers so they run through the dirt again, and make sure all the storm drains in your neighborhood are nice and clear.
Even better, all of this - ESPECIALLY the rain gardens - will also help a ton with flood control!
I'm so serious about how cool this could be, yall.
And people who can't or don't want to do physical stuff for any of these festivals could volunteer to watch children or cook food for the festival or whatever else might need to be done!
Parties afterward to celebrate all the good work done! Community building and direct local improvements to help protect ourselves from climate change!
The possibilities are literally endless, so not to sound like an influencer or some shit, but please DO comment or reply or put it in the notes if you have thoughts, esp on other things we could hold festivals like this for.
Canning festivals. "Dig your elderly neighbors out of the snow" festivals. Endangered species nesting count festival. Plant fruit trees on public land and parks festival. All of the things that I don't know anywhere near enough to think of. Especially in more niche or extreme ecosystems, there are so many possibilities that could do a lot of good
#climate change#climate action#climate crisis#climate hope#solarpunk#hopepunk#hope posting#community building#ecosystem#ecosystem restoration#forest fire#fire prevention#flood#flood prevention#harvest#harvest festival#regenerative agriculture#modern farming#water conservation#meteorology#festival#not news#hope#climate optimism
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
I got emotional reading this. This is the kind of work we need. Working with nature instead of against it to reduce environmental disasters (in this case, it has the added benefit of helping groundwater levels). Working with indigenous groups to rewild land in a way that doesn’t cut human interaction out of the picture.
#Rewilding#Solarpunk#Good news#Hopepunk#conservation#water conservation#We can make the world better#we can fix this
19 notes
·
View notes